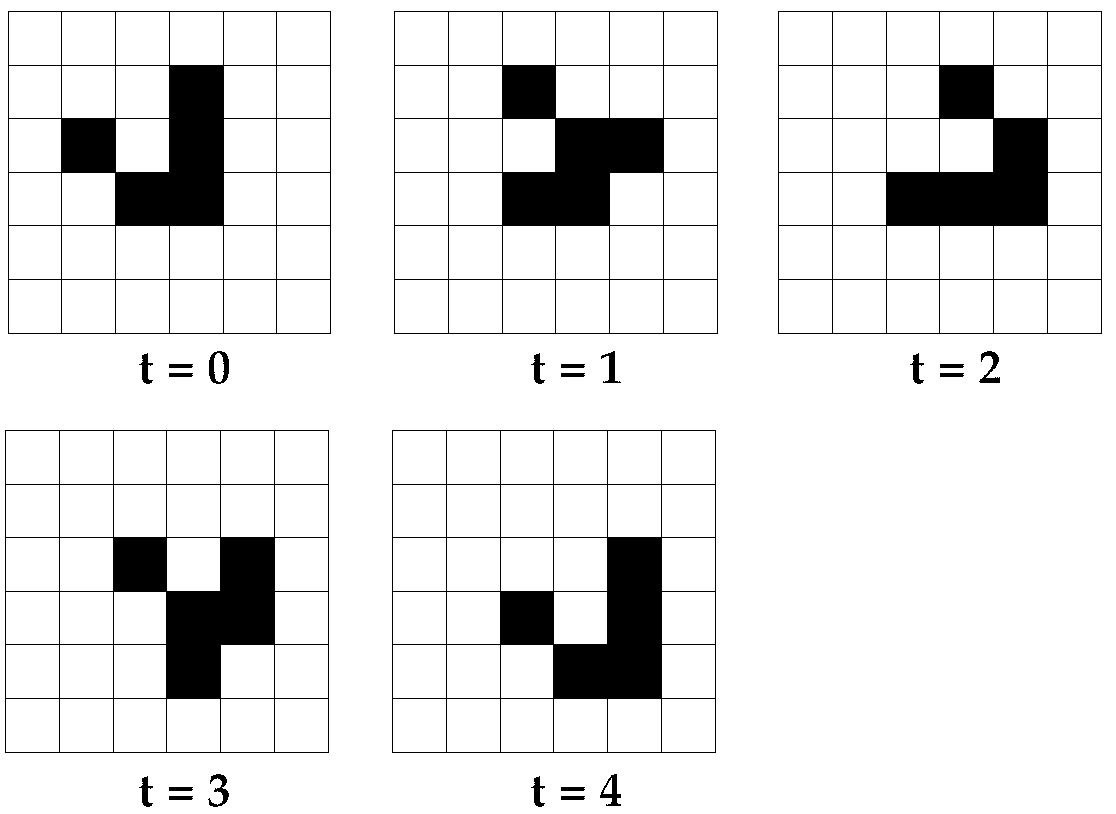El ejemplo toma una cadena de A's y B's arbitrarias y sustituye todo por A's. Cambiando las reglas de las transiciones y los símbolos usados se podría cargar cualquier máquina... Al final se produce una respuesta: Accept o Crash.
Tomada de: http://code.activestate.com/recipes/252486-turing-machine-simulator/
## {{{ http://code.activestate.com/recipes/252486/ (r1)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# (C) 2003 Ryan Phillips
# Uses Python 3
import sys
pr = sys.stdout.write
class MachineTapeException(Exception):
""" Turing Exception Exception """
def __init__(self, value):
Exception.__init__(self)
self.value = value
def __str__(self):
return self.value
class TuringErrorException(Exception):
""" Turing Exception Exception """
def __str__(self):
return "Crash"
class TuringAcceptException(Exception):
""" Turing Accept Exception """
def __str__(self):
return "Accept"
class MachineTape:
def __init__(self, initialString=[], initialPos=0, blank="_"):
""" The Tape uses a simple list. It could easily be changed into a string if
need be """
self.tape = []
self.pos = initialPos
self.blank = blank
self.initialString = initialString
if len(initialString) > 0:
for ch in initialString:
self.tape.append(ch)
else:
self.tape.append(blank)
def reinit(self):
self.__init__(self.initialString)
def move(self, check_char, changeto_char, direction):
""" Only R, L directions are supported """
# check to see if the character under the head is what we need
if check_char != self.tape[self.pos]:
raise MachineTapeException ("Tape head doesn't match head character")
# at this point the head is over the same character we are looking for
# change the head character to the new character
self.tape[self.pos] = changeto_char
if direction == "L":
self.move_left()
elif direction == "R":
self.move_right()
else: raise MachineTapeException ("Direction is invalid")
def read(self):
""" return the character over the head """
return self.tape[self.pos]
def move_left(self):
if self.pos <= 0:
self.tape.insert(-1, self.blank)
self.pos = 0
else:
self.pos += -1
def move_right(self):
self.pos += 1
if self.pos >= len(self.tape): self.tape.append(self.blank)
def show(self):
""" print the tape """
for ch in self.tape:
pr(ch)
pr("\n"); pr(" "*self.pos + "^"); pr("\n")
"""
The program structure for the TM is created with a dictionary.
To step algorithm:
1. Check to see if the length of the string is zero and if we
are in a final state
2. If the currentstate is in the final states then raise an Accept
3. If the currentstate is not in the program then raise an Error
4. Check the head character
5. If the head character is not in the program and in the current state then
raise an Error
6. Retrieve from the dictionary the dest_state, char_out, and movement
7. set the current state to the new state
8. write the tape, and move the head
Program Layout:
[state][char_in] --> [(dest_state, char_out, movement)]
"""
class TuringMachine:
def __init__(self, initialString, finalStates=[], blank="_"):
self.blank = blank
self.tape = MachineTape(initialString)
self.fstates = finalStates
self.program = {}
self.initState = 0
self.state = self.initState
self.lenStr = len(initialString)
def reinit(self):
self.state = self.initState
self.tape.reinit()
def addTransition(self, state, char_in, dest_state, char_out, movement):
if not self.program.has_key(state):
self.program[state] = {}
tup = (dest_state, char_out, movement)
self.program[state][char_in] = tup
def step(self):
""" Steps 1 - 3 """
if self.lenStr == 0 and self.state in self.fstates: raise TuringAcceptException
if self.state in self.fstates: raise TuringAcceptException
if self.state not in self.program.keys(): raise TuringErrorException
""" Steps 4 and 5 """
head = self.tape.read()
if head not in self.program[self.state].keys(): raise TuringErrorException
""" Steps 6 and 7 """
# execute transition
(dest_state, char_out, movement) = self.program[self.state][head]
self.state = dest_state
try:
""" Step 8 """
self.tape.move(head, char_out, movement)
except MachineTapeException, s:
print s
def execute(self):
""" The TM will keep stepping forever until the TM accepts or rejects.
This does allow for looping TM's """
try:
while 1:
m.tape.show()
m.step()
except (TuringErrorException, TuringAcceptException), s:
print s
if __name__ == "__main__":
# machine to convert a string of A's and B's to
# all A's and accept
m = TuringMachine("ABBABB", [1])
m.addTransition(0,'A',0,'A','R')
m.addTransition(0,'B',0,'A','R')
m.addTransition(0,'_',1,'_','L')
# run the TM
m.execute()
## end of http://code.activestate.com/recipes/252486/ }}}